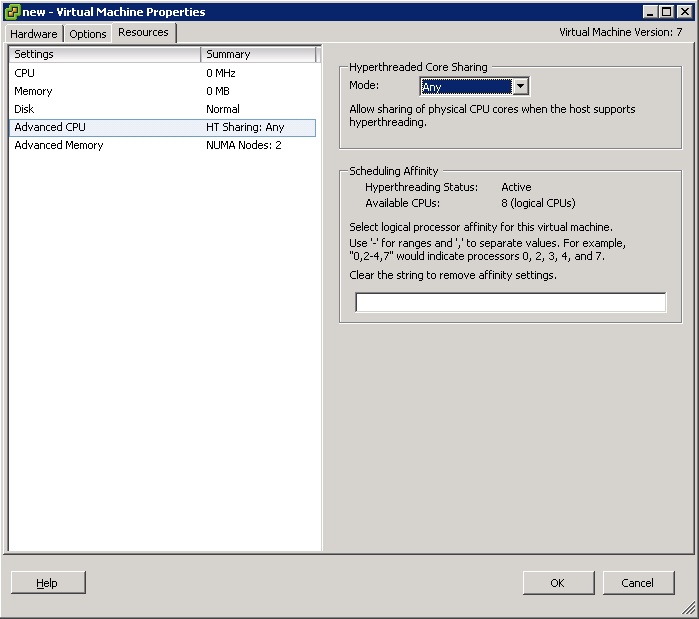
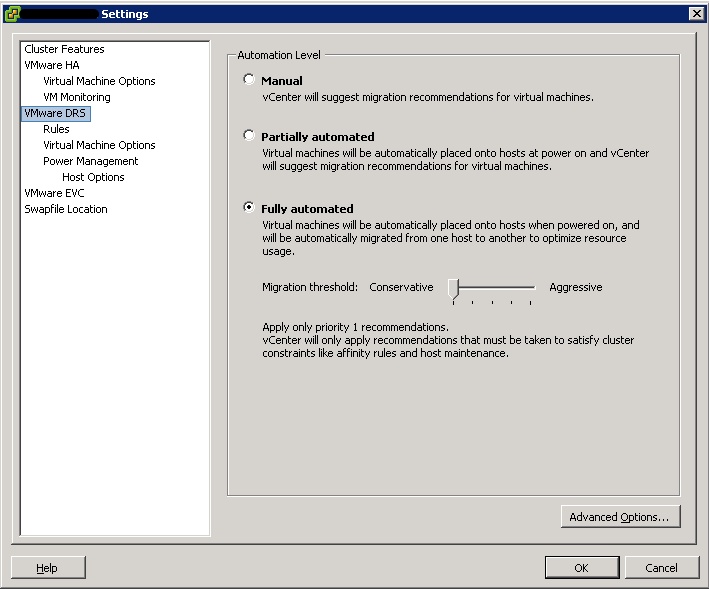
After Setting the VMware DRS settings to Fully automated, the scheduling affinity menu was missing (see figure 1). If you want to change scheduling affinity, set the DRS settings to manual or partial (see figure 2).
Monthly Archives: May 2010
TS Licensing Step-by-Step Guide
How should I prepare to use TS Licensing?
To use TS Licensing to manage TS CALs, you will need to do the following on a server running Windows Server 2008:
- Install the TS Licensing role service.
- Open TS Licensing Manager and connect to the Terminal Services license server.
- Activate the license server.
- Install required TS CALs on the license server.
For a detailed instruction, browse to: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-gb/library/cc754034(WS.10).aspx
Keep in mind that a terminal server running Windows Server 2008 cannot communicate with a license server running Windows Server 2003. However, it is possible for a terminal server running Windows Server 2003 to communicate with a license server running Windows Server 2008.
Windows Disk timeout is not set at default
source: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa997069(EXCHG.80).aspx
Disk timeout is not set at default
The Microsoft® Exchange Server Analyzer Tool reads the following registry entry to determine whether the disk time-out value has been changed from the default value:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesDiskTimeOutValue
If the Exchange Server Analyzer finds the TimeOutValue present and configured with any value other than 10, and the server is non-clustered, a non-default configuration message is displayed. If the Exchange Server Analyzer finds the TimeOutValue present and configured with any value other than 20, and the server is clustered, a non-default configuration message is displayed.
Disk time-out is a registry setting that defines the time that Microsoft Windows® will wait for a hard disk to respond to a command. On a non-clustered system, this key is not present and a default value of 10 seconds is used for all disks. On a Windows cluster, this key is present and uses a default value of 20 seconds. If the time-out time is more than the value in this registry setting, Windows will show an error and will stop disk access. Sometimes, this may be set to a greater value if you are running multipath disk-access software. Multipath software lets you connect multiple physical paths (such as fiber) to a single disk drive for redundancy. Multipath software manages the multiple physical connections so that Windows handles only a single handle to the disk.
Installing host bus adapters (HBA) or other storage controllers can cause this key to be created and configured. When you install or reinstall these drivers, the TimeOutValue registry value is overwritten with the value that is required by those drivers. You may have to contact the hardware vendor to determine the correct TimeOutValue registry value for your configuration.
To revert to the default configuration
- Open a registry editor, such as Regedit.exe or Regedt32.exe.
- Navigate to:
HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetServicesDiskTimeOutValue
- In the right pane, delete the TimeOutValue entry. Alternatively, double-click the TimeOutValue entry and set it to one of the following values:
- On a non-clustered server, set the value to 10.
- On a clustered server, set the value to 20.
- If your hardware manufacturer recommends a different value for either a clustered or non-clustered system, use the value from your hardware manufacturer instead.
- Close the registry editor, and then restart the computer for the change to take effect.
Many Acrobat 7.0.x acr*.tmp files created in the WindowsTemp folder
On a system there are many acr*.tmp files in the windostemp folder. After searching for this problem we found that this has to do with the windows indexing service and acrobat 7.
Windows Indexing Service indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers, improving search performance. Windows Indexing Service calls the PDF iFilter to extract text from PDF files. This process causes Acrobat to generate a significant number of temporary files depending on the content of the PDF files. When you disable the Windows Indexing Service or the PDF iFilter, the creation of these temporary files is stopped.
Because we can not disable the index service we upgraded acrobat to a newer version.
For other solutions see the following article:
http://kb2.adobe.com/cps/330/330414.html
Solution 1:Upgrade to Acrobat 8.0 (Professional or Standard) or Adobe Reader 8.0.
— To purchase an upgrade from Adobe, visit the Adobe Store at http://store.adobe.com/store/ , click Acrobat Family and choose Acrobat Standard or Acrobat Professional.
— To locate an authorized reseller, visit the Adobe website at www.adobe.com/store/customerregistration/other_places.jhtml .
— To download the free Adobe Reader 8.0, visit the Adobe website at www.adobe.com/products/acrobat/readstep2.html .
Solution 2: Rename or delete the PDF iFilter indexing plug-in.
For Adobe Reader 7.0.x:
1. From the Start menu, select Search and then select All Files Or Folders.
2. In the All Or Part Of The File Name field, type AcroRdIF.dll.
3. After the search result(s) appears, right-click the AcroRdIF.dll file and select Rename.
4. Rename AcroRdIF.dll to AcroRdIF.old.
For Acrobat Standard,and Pro 7.0.x and Acrobat 3D:
1. From the Start menu, select Search and then select All Files Or Folders.
2. In the All Or Part Of The File Name field, type AcroIF.dll.
3. After the search result(s) appears, right-click the AcroIF.dll file and select Rename.
4. Rename AcroIF.dll to AcroIF.old.
Solution 3: Stop the Windows Indexing Service.
On Windows XP:
1. From the Start menu, select Search, and the select Change Preferences.
2. Select Without Indexing Service.
3. Select “No, do not enable Indexing Service.”
On Windows 2000:
1. From the Start menu, select Search > For Files Or Folders.
2. Select Indexing Service.
3. Select “No, do not enable Indexing Service.”
Note: Disabling the Indexing Service may make searching for files or folders on your machine somewhat slower.
Blackberry leaves bba**.tmp files in the temp folder
If you have a lot of bba**.tmp files under your temp directory (c:windowstemp) the blackberry attachment service isn’t cleaning it’s temporary files anymore. Install at least service pack 5 on your Blackberry 4 server.
Offcourse you can manually delete these files, but after a while they will come back.
See this post