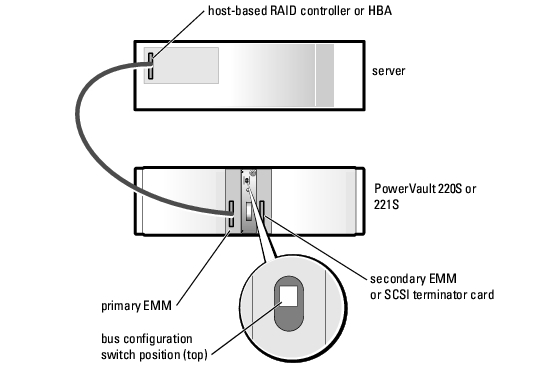
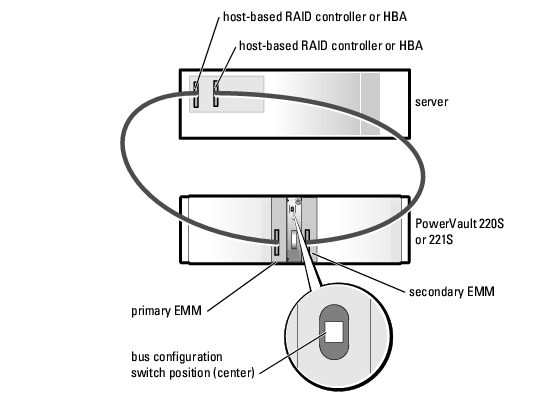
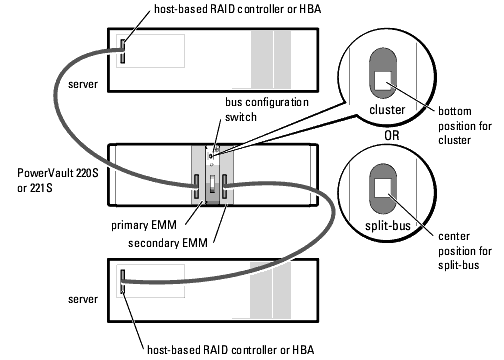
More information: ftp://ftp.software.ibm.com/systems/support/system_x_pdf/59y7287.pdf
Connecting storage expansion enclosures at the end (bottom) of a drive loop
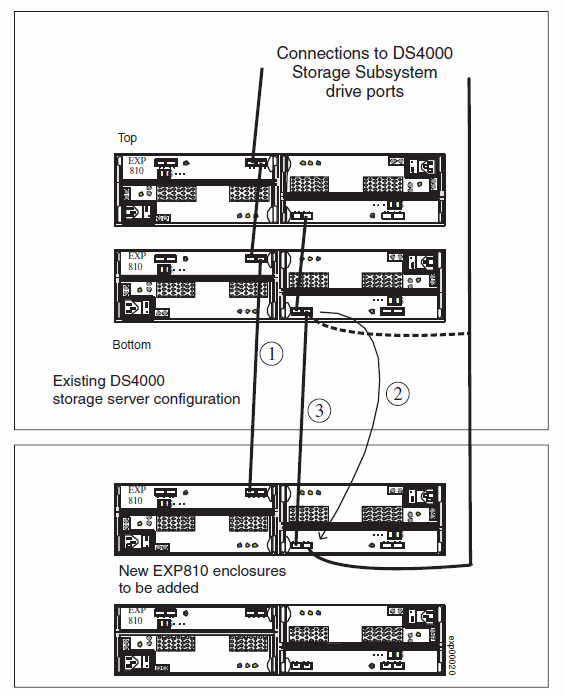
To add a 16-drive expansion enclosure, for example, an EXP810 or EXP420 to the DS4000 subsystem configuration, you basically follow the same procedure as in adding the 14-drive enclosure to a DS4000 subsystem configuration; however, the port connections on the 16-drive enclosure are different, as illustrated in Figure 4and the three steps that follow it.
| 1. | Insert the small form-factor pluggables (SFPs) or gigabit interface converters (GBICs) into only those ports that you intend to use. Do not leave GBICs or SFPs inserted into port connectors without connecting them to other ports using cables. |
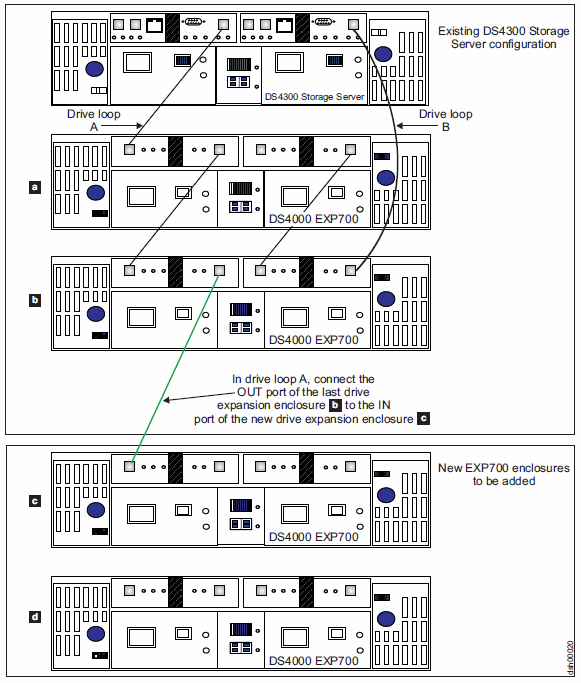
| 2. | Extend one of the drive loops (that is, drive loop A) in a DS4000 storage subsystem redundant drive loop pair by connecting the OUT port of the last storage expansion enclosure to the IN port of the storage expansion enclosure as shown in Figure 1Note: The port name on an EXP810 is not labeled IN. See Figure 4 for details.
Attention: Carefully reconfigure only one drive loop at a time, making sure that the drive loop that you modify is correctly connected and in Optimal state before you attempt to reconfigure another drive loop. Take this precaution to prevent the arrays from being inadvertently failed by the DS4000 storage subsystem controllers, which happens when two or more drives in the arrays cannot be reached through either drive loop in the redundant drive loop pair. |
| 3. | Power on the added storage expansion enclosure unit. |
| 4. | Wait a few seconds; verify that the port bypass LEDs of all of the ports in drive loop A, now extended to the storage expansion enclosure, are not lit. Using the DS Storage Manager Client Subsystem Management window, verify that the storage expansion enclosure is added and displayed in the Logical/Physical view of the window.Correct any errors before you proceed to step 5. For port bypass, complete the following steps:
Call IBM support for assistance, if the problem remains. |
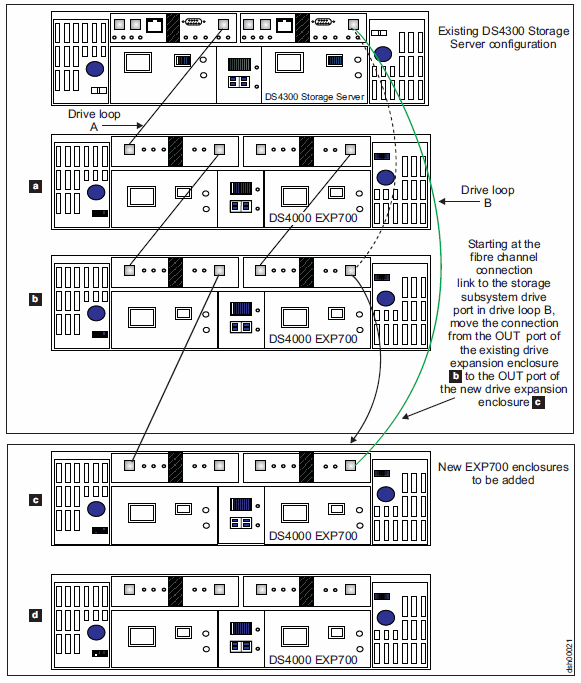
| 5. | In the other drive loop (drive loop B) in a DS4000 storage subsystem redundant drive loop pair, remove the connection from the storage subsystem drive loop port to the OUT port of the last storage expansion enclosure and connect it to the OUT port of the drive enclosure as shown in Figure 2.Note: The port name on an EXP810 is not labeled OUT. See Figure 4 for details. |
| 6. | Wait a few seconds; verify that the port bypass LEDs of the two ports in the connection between the storage subsystem drive loop port and the OUT port of the drive enclosure are not lit. Using the DS Storage Manager Client Subsystem Management window, verify that the drive enclosure does not indicate the Drive enclosure lost redundancy path error. See step 4 for possible corrective actions, as needed.Note: The existing storage expansion enclosures are shown with “Drive enclosure lost redundancy” path errors until you establish the Fibre Channel cabling connection that is described in step 7. |
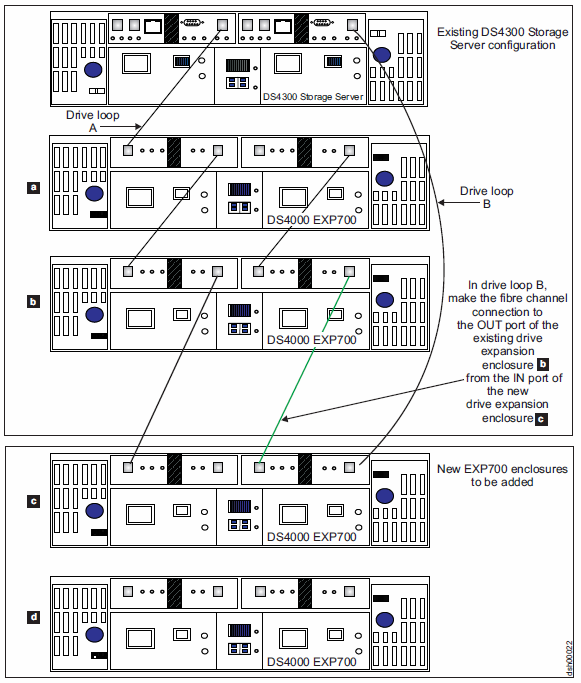
| 7. | In drive loop B, cable the drive enclosure IN port to the OUT port of the last enclosure in the already functioning storage expansion enclosure drive loop, as shown in Figure 3. |
| 8. | Wait a few seconds; verify that the port bypass LEDs of all of the ports in drive loop B to which you have added a connection are not lit. Using the DS Storage Manager Client Subsystem Management window, verify that all of the drive enclosures in the DS4000 redundant drive loop pair to which the enclosure was added do not report the “Drive enclosure lost redundancy” path error. |