see Find IP addresses using Exchange SMTP relay – ALI TAJRAN
To make this work, your SMTP relay logging should be enabled.
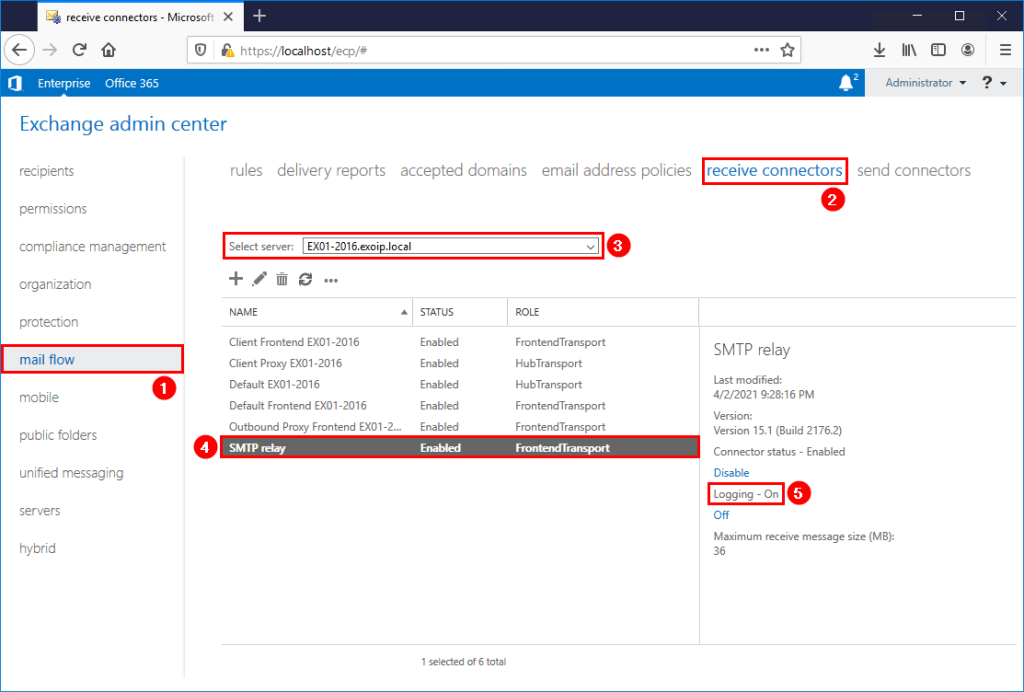
The script will look into your logfiles and export all IP address which have been using the relay service. If your loglocations is different then the default (C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd\ProtocolLog\SmtpReceive), make sure to alter it in the script.
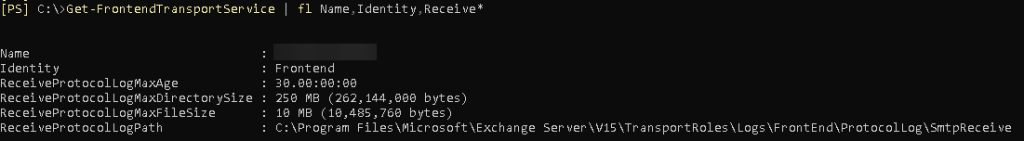
Your logfile location can be found by executing the following powershell script:
Get-FrontendTransportService | fl Name,Identity,Receive*
Prepare SMTP-Review PowerShell script
Create two folders on the Exchange Server (C:) drive:
- Temp
- Scripts
Copy and paste the below code into Notepad. Give it the name SMTP-Review.ps1 and place it in the C:\scripts folder.
<#
.SYNOPSIS
SMTP-Review.ps1
.DESCRIPTION
Script is intended to help determine servers that are using an Exchange server to connect and send email.
This is especially pertinent in a decommission scenario, where the logs are to be checked to ensure that
all SMTP traffic has been moved to the correct endpoint.
.LINK
www.alitajran.com/find-ip-addresses-using-exchange-smtp-relay
.NOTES
Written by: ALI TAJRAN
Website: www.alitajran.com
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/alitajran
.CHANGELOG
V1.00, 04/05/2021 - Initial version
V2.00, 03/28/2023 - Rewrite script to retrieve results faster
#>
# Clears the host console to make it easier to read output
Clear-Host
# Sets the path to the directory containing the log files to be processed
$logFilePath = "C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd\ProtocolLog\SmtpReceive\*.log"
# Sets the path to the output file that will contain the unique IP addresses
$Output = "C:\temp\IPAddresses.txt"
# Gets a list of the log files in the specified directory
$logFiles = Get-ChildItem $logFilePath
# Gets the number of log files to be processed
$count = $logFiles.Count
# Initializes an array to store the unique IP addresses
$ips = foreach ($log in $logFiles) {
# Displays progress information
$percentComplete = [int](($logFiles.IndexOf($log) + 1) / $count * 100)
$status = "Processing $($log.FullName) - $percentComplete% complete ($($logFiles.IndexOf($log)+1) of $count)"
Write-Progress -Activity "Collecting Log details" -Status $status -PercentComplete $percentComplete
# Displays the name of the log file being processed
Write-Host "Processing Log File $($log.FullName)" -ForegroundColor Magenta
# Reads the content of the log file, skipping the first five lines
$fileContent = Get-Content $log | Select-Object -Skip 5
# Loops through each line in the log file
foreach ($line in $fileContent) {
# Extracts the IP address from the socket information in the log line
$socket = $line.Split(',')[5]
$ip = $socket.Split(':')[0]
# Adds the IP address to the $ips array
$ip
}
}
# Removes duplicate IP addresses from the $ips array and sorts them alphabetically
$uniqueIps = $ips | Select-Object -Unique | Sort-Object
# Displays the list of unique IP addresses on the console
Write-Host "List of noted remove IPs:"
$uniqueIps
Write-Host
# Writes the list of unique IP addresses to the output file
$uniqueIps | Out-File $OutputIn Line 27, change the path to the receive protocol log path you searched for in the previous step.
Run SMTP-Review PowerShell script
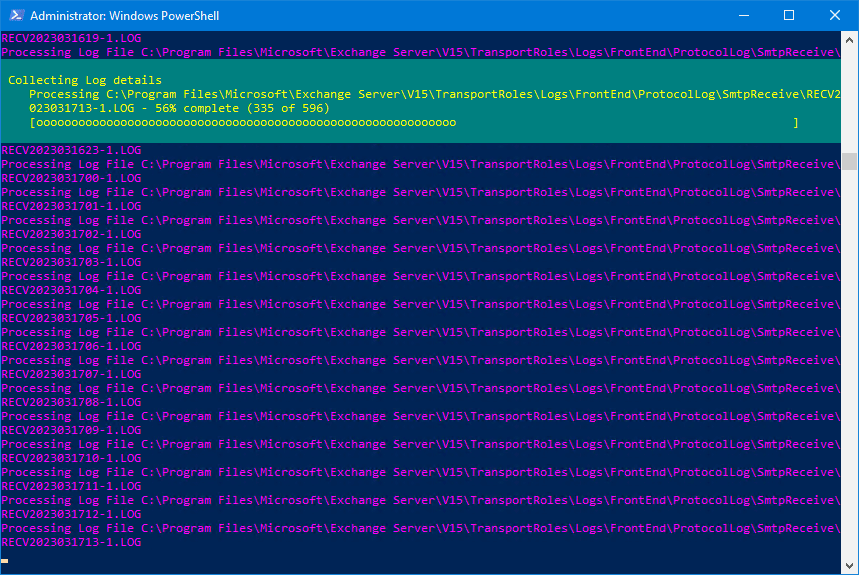
Run PowerShell as administrator and run the SMTP-Review.ps1 PowerShell script.
The script will go through all the files, and after it finishes, you will see which IP addresses use the SMTP relay in the console output. Also, it will generate an IPAddresses.txt file with the IP addresses in the C:\temp folder.
Make a note of the IP addresses and adjust the SMTP field in the printers, applications, and servers to the new SMTP relay record.